large-toothed aspen
large-toothed aspen - Populus grandidentata
This fast-growing, short-lived species is extremely important in regenerating forest growth after clearing or burning. Its vigorous roots help to retain soil and trap moisture, and its branches provide shade for other species. Large-toothed aspen may resemble trembling aspen, but can be distinguished by their larger leaves edged with large, coarse, and uneven teeth. Moose, elk, muskrats, and rabbits, (amongst many other animals), will eat the buds, bark, and twigs year round, while birds enjoy the downy fruits.
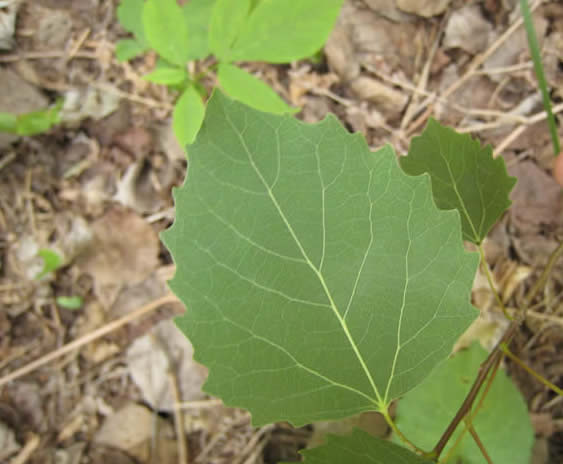

The specific name grandidentata means large-toothed, directly translating into the common name. Like trembling aspen, these leaves are attached by flat stalks, which make them tremble in even the lightest breeze. Photo by Sean Fox.

Bark of the large-toothed aspen is smooth and usually grey. In comparison to the trembling aspen, the mature bark is much darker, growing furrowed with age. Photo by Jesse Wolf.
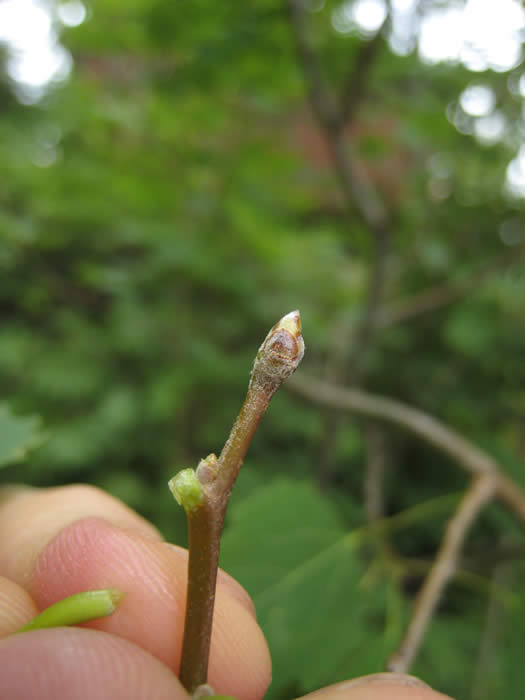

Buds of the large-toothed aspen are 7-8 mm long, dull brown in colour and slightly hairy. Photo by Sean Fox.
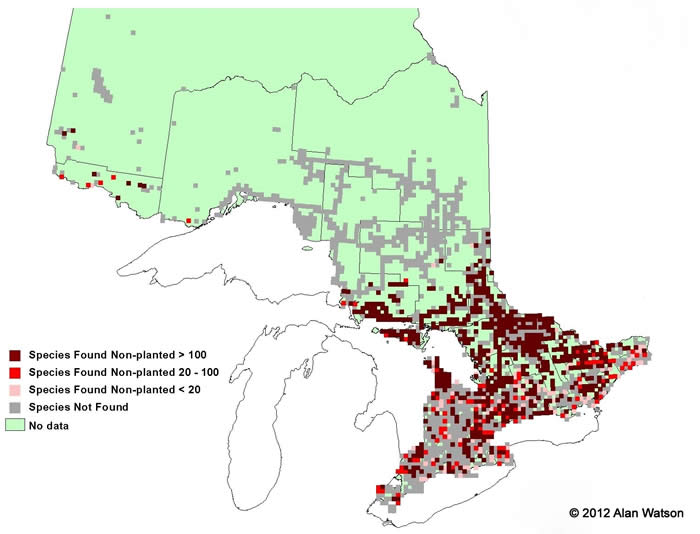
Ontario Tree Atlas map of non-planted Largetooth Aspen. 1995-1999.
References
Farrar, J.L.. 1995. Trees in Canada. Fitzhenry & Whiteside Ltd. Toronto. ON. 504 pp.
Kershaw, L. 2001. Trees in Ontario: Including tall shrubs. Lone Pine Publishing. Edmonton. AB. 240 pp
Muma, W. 2011. Ontario Trees and Shrubs. [Online] Available: www.ontariotrees.com
OMNR, 2011. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources: Ontario Tree Atlas. [Online] Available: http://www.mnr.gov.on.ca/en/Business/ClimateChange/2ColumnSubPage/267027.html
OMNR, 2008. Ontario’s Biodiversity: Species at Risk.