white oak - Quercus alba
White oak is valued as one our most important commercial hardwoods. All oaks have very hard, durable, and elastic wood, and white oak has traditionally been used as a watertight wood in shipbuilding, and casks and barrels for whiskies and wines. White oak can be distinguished from the common red oak by their deep, rounded lobes compared to sharply toothed lobes (think 5 letters in WHITE and ROUND). White oak can be differentiated from the similar bur oak because the leaves are a very bright green, with much deeper lobes than bur oak. White oak acorns are sweet and edible when raw, and were traditionally an important staple food for Indigenous populations. White oak acorns are still used today, ground into flour for baking or roasted as a caffeine-free coffee substitute.

White oak bark is flaky or scaly, and grey when mature. Red oak and its closer relatives have smooth bark. Photo by Jesse Wolf.
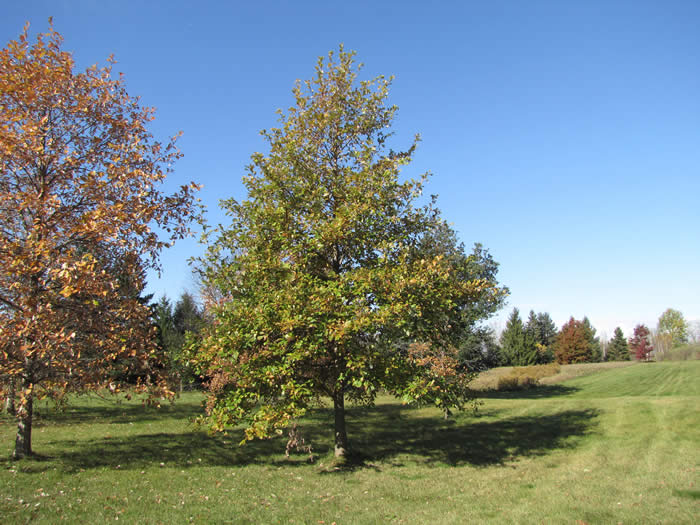

The white oak can grow up to be 35 m in height, 1.2 m in diameter, and several hundred years old. This tree is unique as it can be free from branches for two thirds of its total height. Photo by Chris Earley.
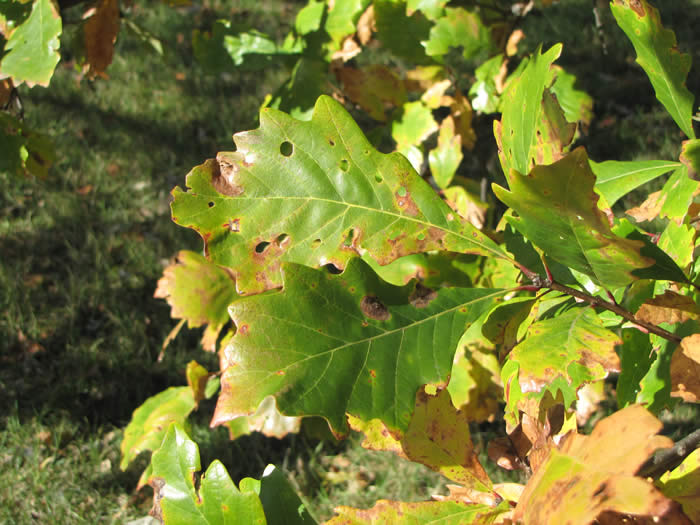

White oak leaves are hairless when mature and have 5-9 deep, rounded lobes, leaves measured at 10-20 cm on average. Photos by Chris Earley.
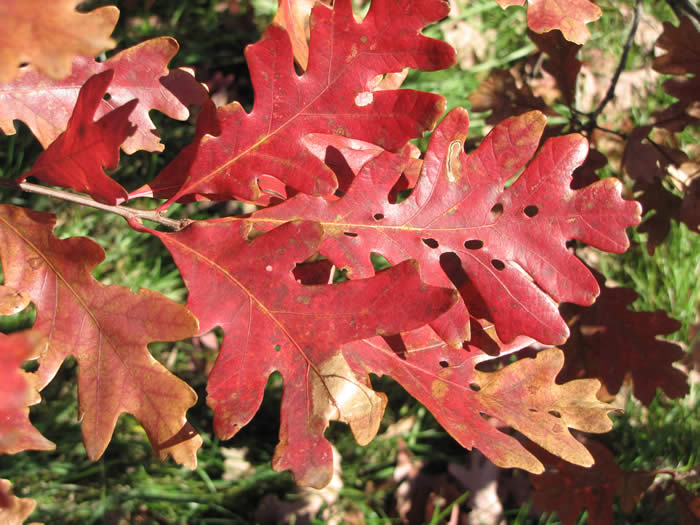

They sometimes turn a beautiful purple-red in the fall. Photo by Chris Earley.
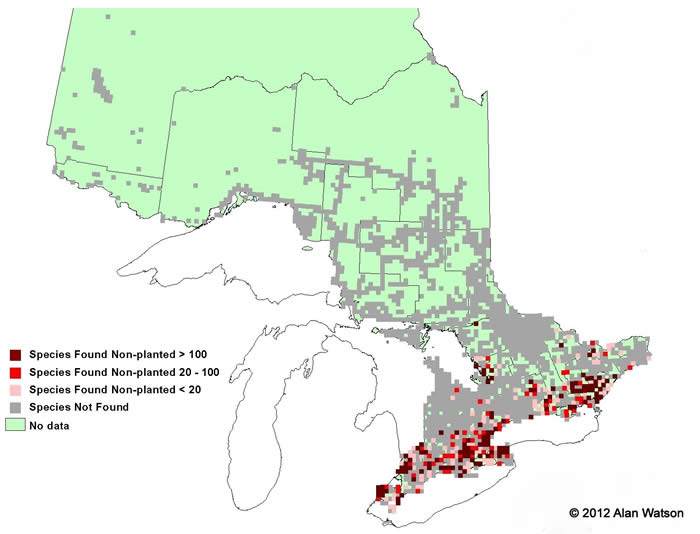
Ontario Tree Atlas map of non-planted White Oak. 1995-1999.
Return to tree listing page [1]
References
Farrar, J.L.. 1995. Trees in Canada. Fitzhenry & Whiteside Ltd. Toronto. ON. 504 pp.
Kershaw, L. 2001. Trees in Ontario: Including tall shrubs. Lone Pine Publishing. Edmonton. AB. 240 pp
Muma, W. 2011. Ontario Trees and Shrubs. [Online] Available: www.ontariotrees.com
OMNR, 2011. Ontario Ministry of Natural Resources: Ontario Tree Atlas. [Online] Available: http://www.mnr.gov.on.ca/en/Business/ClimateChange/2ColumnSubPage/267027.html
OMNR, 2008. Ontario’s Biodiversity: Species at Risk.

